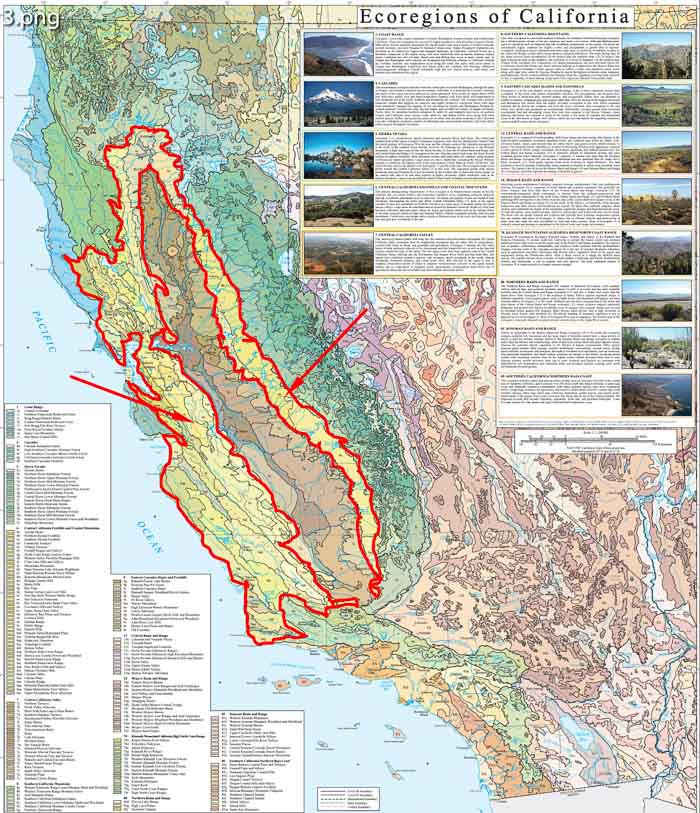
California has tremendous ecological and biological diversity. It contains offshore islands and coastal lowlands, large alluvial valleys, forested mountain ranges, deserts, and various aquatic habitats.
California is divided into 13 main ecological regions and 177 sub-regions. Unique in topography, soil depth, pH, elevation, light, and hydrology, each region provides a rich variety of ecological habitats, supporting many native plant species.
The Central California Foothills and Coastal Mountains region is characterized by its Mediterranean climate of hot dry summers and cool moist winters, and an associated vegetative cover comprising primarily chaparral and oak woodlands; grasslands occur in some low elevations and patches of pine are found at high elevations. Surrounding the lower and flatter Central California Valley, most of the region consists of open low mountains or foothills, but there are some areas of irregular plains and some narrow valleys. Large areas are ranchland and are grazed by domestic livestock. Relatively little land has been cultivated, although some valleys are major agricultural centers such as the Salinas Valley or the wine vineyard centers of Napa and Sonoma Valleys. Natural vegetation includes coast live oak woodlands, Coulter pine, and unique native stands of Monterey pine in the west, and blue oak, black oak, and grey pine woodlands in the east.
The Central California Foothills and Coastal Mountains encompass:
- The Tuscan Flows ecoregion is a gently southwest-sloping plateau with some steep canyons and a few steep volcanic cones.
- The Northern Sierran Foothills ecoregion consists of moderately steep to steep mountains and hills at the western foot of the northern and central Sierra Nevada.
- The moderately steep hills and low mountains of the Southern Sierran Foothills ecoregion represent a transition from the Central California Valley to the Sierra Nevada.
- The Camanche Terraces, on gently sloping to moderately steep hills and dissected terraces along the eastern edge of the Central California Valley downslope from the central Sierra Nevada foothills.
- The Tehama Terraces ecoregion forms a dissected plain between the coastal hills to the west and the western margin of the Sacramento Valley.
- The Foothill Ridges and Valleys ecoregion, includes ridges, steep hills, and narrow valleys in the interior northern California Coast Ranges. It extends from the Vaca Mountains and Blue Ridge in the south to the Bald Hills in the north near the Klamath Mountains.
- The North Coast Range Eastern Slopes ecoregion is located along the steep north-trending eastern edge of the Northern Coast Range mountains with sedimentary and ultramafic rocks.
- The Western Valley Foothills/Dunnigan Hills ecoregion consists of the Dunnigan Hills, English Hills, Capay Valley, and other low hills or terraces adjacent to the western margin of the Central California Valley ecoregion.
- The Clear Lake Hills and Valleys ecoregion, which is a relatively low elevation area of the northern Coast Ranges, is surrounded by ecoregions with higher elevation hills and mountains and greater relief.
- The Mayacmas Mountains ecoregion is an interior coastal range that contrasts with the Ukiah/Russian River Valleys to the west and Clear Lake Hills and Valleys to the east.
- The Napa-Sonoma-Lake Volcanic Highlands includes the volcanic terrain around Mount Konocti and the mostly volcanic terrain that extends to the southeast.
- The Napa-Sonoma-Russian River Valleys ecoregion is lower, flatter, more populated, and has more cropland, vineyards, and orchards than the surrounding more mountainous ecoregions.
- The Sonoma-Mendocino Mixed Forest ecoregion is characterized primarily by a mixed hardwood forest. It includes tanoak, black oak, madrone, Oregon white oak, Douglas-fir, and only a few small areas of redwoods.
- The Bodega Coastal Hills ecoregion is mostly all grassland and coastal scrub.
- The Marin Hills ecoregion consists of mountains and hills between San Francisco Bay and the San Andreas Fault.
- The Bay Flats ecoregion includes the near-water flats around San Pablo Bay in the north and those at the southern end of San Francisco Bay.
- The low-elevation Suisun Terraces and Low Hills ecoregion surrounding Suisun Bay, upland from the lower part of the Delta. A few low hills occur, such as the Portrero Hills and Montezuma Hills.
- The East Bay Hills/Western Diablo Range ecoregion consists of the East Bay Hills to the east of the Berkeley-Oakland-Hayward urban area, Mount Diablo and the Black Hills area farther east, as well as the hills of the western Diablo Range.
- The San Francisco Peninsula ecoregion occurs at the northern end of the peninsula, with a climate affected greatly by marine influence.
- The Bay Terraces/Lower Santa Clara Valley ecoregion is an urbanized area on alluvial plains that wrap around San Francisco Bay between the East Bay Hills ecoregion on the east and the Leeward Hills ecoregion to the west.
- The Livermore Hills and Valleys ecoregion consists of the Livermore, Amador, and San Ramon Valleys and the low hills that surround them.
- The Upper Santa Clara Valley ecoregion is a low-relief alluvial plain in the upper Santa Clara Valley, including the San Benito Valley.
- The coastal Monterey Bay Plains and Terraces ecoregion occurs on alluvial plains and terraces that wrap around Monterey Bay.
- The Leeward Hills ecoregion is an area of mountains and hills with rounded ridges, steep and moderately steep sides, and narrow canyons.
- The Gabilan Range ecoregion contains steep mountains between the San Andreas Fault on the northeast and the Salinas Valley on the southwest.
- The Diablo Range ecoregion includes mountains with rounded ridges and steep to moderately steep sides, along with narrow canyons and valleys.
- The Eastern Hills ecoregion includes the low, steep mountains and foothills on the eastern side of the Diablo Range, including the Panoche, Ciervo, and Kettleman Hills, and Avenal Ridge at the southern end.
- The Pleasant Valley/Kettleman Plain ecoregion contains disjunct small valleys and relatively flat plains that contrast with the steeper, adjacent hills.
- The Temblor Range/Elk Hills ecoregion contains steep mountains and moderately steep hills around the Temblor Range and the lower, gentler Elk Hills.
- The Grapevine Transition ecoregion is an intermediate region between the Southern California Mountains and Central California Valley.
- The Tehachapi Foothills ecoregion consists of moderately steep to steep mountains and hills on mostly granitic terrain.
- The Salinas Valley ecoregion includes gently sloping alluvial plains, stream terraces, and nearly level floodplains of the Salinas Valley.
- The Northern Santa Lucia Range
- The Santa Lucia Coastal Forest and Woodland ecoregion is a near-coastal zone that stretches from Carmel Bay in the north to Salmon Creek in the south.
- The Interior Santa Lucia Range ecoregion stretches southeast from near Greenfield in the Salinas Valley ecoregion, to near the Sisquoc River, east of the Santa Maria Valley ecoregion.
- The Southern Santa Lucia Range includes northwest-trending mountains and hills with rounded ridges, steep sides, and narrow canyons.
- The Paso Robles Hills and Valleys ecoregion is a dissected plain with low, rolling to moderately steep hills.
- The Cuyama Valley ecoregion consists of alluvial fans, pediments, and terraces along the Cuyama River.
- The Carrizo Plain ecoregion is a nearly level to very gently sloping alluvial plain with low hills on the margins.
- The Caliente Range is characterized by steep mountains with narrow canyons.
- The moderately steep to steep hills of the Solomon-Purisima-Santa Ynez Hills ecoregion has a mosaic of coastal sage scrub, chaparral, and oak woodland, interspersed with some grasslands used for cattle ranching.
- The Santa Maria/Santa Ynez Valleys ecoregion occurs on alluvial plains along the Santa Maria and Santa Ynez Rivers.
- The Upper Sacramento River Alluvium ecoregion includes the floodplains and terraces of the Sacramento River and lower Cottonwood Creek in the area between Redding and Red Bluff.
The Central California Foothills and Coastal Mountains ecoregion lies in Climate Zones 7, 14, 15, 16, and 17.
According to the U.S. Forest Service, Invasive species have contributed to the decline of 42% of U.S. endangered and threatened species, and 18% of U.S. endangered or threatened species. Invasive species compete directly with native species for moisture, sunlight, nutrients, and space. They displace and alter native plant communities, degrade wildlife habitat and water quality, and potentially lead to increased soil erosion.
The federal government has estimated that nearly 25 percent of the 20,000 plant species native to North America are at risk of extinction, many of these through habitat loss. You can help reverse this trend by planting great native plants in your garden.
A plant is considered native if it has occurred naturally in a particular region or ecosystem without human introduction. There are many benefits to growing native plants.
- First, these plants are better adapted to soils, moisture, and weather than exotic plants that evolved in other parts of the world. They need fewer fertilizers, and pesticides or use less water.
- Second, they are unlikely to escape and become invasive, destroying natural habitats.
- Third, they support wildlife, providing shelter and food for native birds and insects, while exotic plants do not.
Here is a list of California native perennials that are well-suited for plantings in shady gardens of the Central California Foothills and Coastal Mountains.
- Never collect native plants from the wild as it will deplete natural ecosystems.
- When possible, plant species grown straight from local seed sources. These native originals are the best choice, as they co-evolved with specific wildlife, which supports migration, breeding, and other seasonal interdependencies.
While every effort has been made to describe these plants accurately, please keep in mind that height, bloom time, and color may differ in various climates. The description of these plants has been written based on numerous outside resources.
